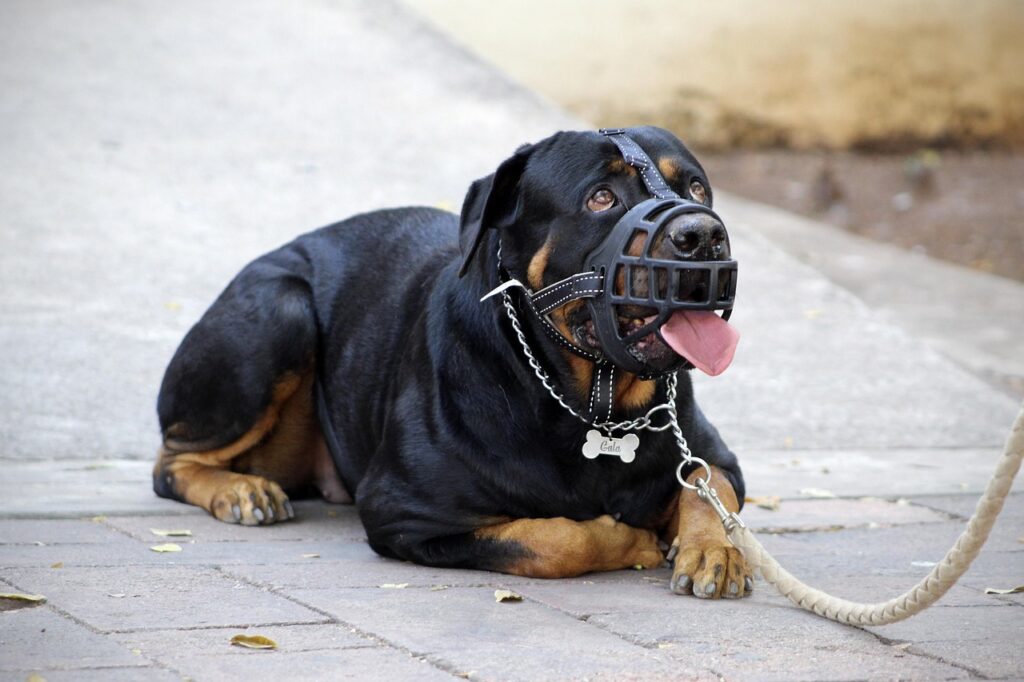
Aggressive dog behavior is a challenge faced by many pet owners, and addressing it requires a comprehensive understanding of the root causes and effective strategies. While aggression can be alarming, it is often a form of communication used by dogs to express discomfort, fear, or dominance. Identifying the underlying factors and implementing appropriate management techniques can help mitigate aggressive behaviors and foster a harmonious relationship between dogs and their owners.
Identifying the Causes of Aggression
Before implementing strategies to manage aggression, it’s crucial to identify the potential causes. Aggression in dogs can stem from various factors, including:
Fear and Anxiety
Fear-induced aggression is common when a dog perceives a threat. This can occur due to past traumatic experiences, lack of socialization, or environmental changes. Dogs may resort to aggression as a defense mechanism to protect themselves.
Territorial Behavior
Dogs are naturally territorial animals. Aggression may occur when a dog feels its territory is being invaded. This can happen when new pets or people enter their space.
Resource Guarding
Some dogs exhibit aggression to protect valuable resources such as food, toys, or even their owners. Resource guarding is a natural instinct, but it can become problematic if not managed properly.
Social Aggression
Social hierarchy plays a significant role in canine behavior. Dogs may display aggression to establish dominance or challenge the authority of other dogs or humans.
Pain and Health Issues
Pain or underlying health problems can lead to irritability and aggression. If a dog suddenly becomes aggressive, it’s essential to rule out medical issues by consulting a veterinarian.
Strategies for Managing Aggressive Behavior
Once the cause of aggression is identified, implementing a tailored strategy is key to managing and reducing aggressive behavior. The following strategies can be effective:
Behavioral Training
Positive reinforcement training is a powerful tool in managing aggression. Rewarding desired behavior and redirecting unwanted behavior helps in modifying a dog’s response to triggers. Consistency and patience are crucial in this approach.
Desensitization and Counter-Conditioning
Gradual exposure to the source of aggression, combined with positive reinforcement, can help desensitize a dog to triggers. Counter-conditioning involves changing the dog’s emotional response to a trigger from negative to positive.
Socialization
Early socialization is essential in preventing aggression. Introducing puppies to various environments, people, and other animals helps them develop confidence and reduces fear-based aggression.
Management Techniques
In some cases, management strategies are necessary to prevent aggressive incidents. This can include using leashes, muzzles, or creating safe spaces where a dog can retreat when feeling threatened.
Professional Guidance
Consulting a professional dog trainer or behaviorist can provide valuable insights and personalized strategies. These experts can assess the dog’s behavior, identify triggers, and develop a customized training plan.
Implementing Positive Reinforcement Techniques
Positive reinforcement is a cornerstone of modern dog training. It involves rewarding a dog for exhibiting desired behaviors, thereby encouraging those behaviors to be repeated. When managing aggression, positive reinforcement can be particularly effective in reshaping a dog’s response to triggers.
Using Treats and Praise
Treats and verbal praise are powerful motivators for dogs. When a dog responds positively to a command or remains calm in the presence of a trigger, offering a treat and praise reinforces the behavior. Over time, the dog learns to associate positive experiences with previously perceived threats.
Clicker Training
Clicker training is a form of positive reinforcement where a clicker sound is used to mark desired behavior, followed by a reward. This method provides clear communication between the dog and owner, making it easier for the dog to understand which behaviors are encouraged.
Building Trust and Confidence
Aggressive behavior often stems from fear or insecurity. Building trust and confidence through positive reinforcement can significantly reduce aggression. Consistent training sessions, exposure to new experiences, and reinforcing positive interactions help in boosting a dog’s confidence.
Addressing Specific Types of Aggression
Different types of aggression require tailored approaches for effective management. Understanding the nuances of each type can aid in developing targeted strategies.
Fear-Based Aggression
For dogs exhibiting fear-based aggression, creating a safe and predictable environment is crucial. Gradual exposure to fear-inducing stimuli, paired with positive reinforcement, can help desensitize the dog and reduce fear responses.
Territorial Aggression
Territorial aggression can be addressed by establishing clear boundaries within the home. Consistent training, using commands like “sit” and “stay,” can help a dog understand acceptable behaviors. Additionally, introducing new pets or people gradually and under controlled conditions can prevent territorial disputes.
Resource Guarding
Resource guarding requires careful management to prevent aggressive incidents. Teaching commands like “leave it” or “drop it” can help manage resource guarding behavior. Creating a structured routine for feeding and playtime can also reduce anxiety related to resource guarding.
Social Aggression
Social aggression often involves establishing dominance. Implementing consistent training and reinforcing a hierarchy where the owner is the leader can help manage social aggression. Ensuring that dogs understand commands and respond appropriately reinforces the owner’s authority.
The Role of Consistency and Patience
Managing aggressive behavior in dogs is a gradual process that requires consistency and patience. It’s essential to understand that behavioral changes take time, and progress may be slow. Consistently applying training techniques, maintaining a calm demeanor, and celebrating small victories contribute to long-term success.
Setting Realistic Expectations
Every dog is unique, and the time required to see significant improvements varies. Setting realistic expectations and celebrating incremental progress can prevent frustration and keep both the owner and the dog motivated.
Maintaining a Positive Environment
Creating a positive and stress-free environment is crucial for managing aggression. Dogs are highly perceptive and can pick up on their owner’s emotions. Maintaining a calm and positive demeanor during training sessions fosters a sense of security for the dog.
Conclusion
Effective management of aggressive dog behavior involves understanding the underlying causes, implementing tailored strategies, and maintaining a consistent and patient approach. By utilizing positive reinforcement techniques, addressing specific types of aggression, and fostering a positive environment, pet owners can create a harmonious relationship with their dogs. Seeking professional guidance when needed ensures that both the dog and owner receive the support necessary for a successful behavior modification journey. With dedication and perseverance, aggressive behavior can be transformed, allowing dogs to thrive in a loving and supportive environment.
#ChatGPT assisted in the creation of this article.